Genetically Informed Ancestry using EIGENSTRAT
Published:
In creating polygenic risk scores in Wang et al., 2021, patient population was subdivided into those with European and African descent.
This was performed using a technique called “Genetically Informed Ancestry”, which is the subject of this blog post.
Background on EIGENSOFT
EIGENSOFT is a software developed by Alkes Price, a Professor of Statistical Genetics at Harvard School of Public health.
The software contains, among other things, a component with the “EIGENSTRAT stratification correction method”. The EIGENSTRAT method uses principal components analysis (PCA) to model ancestry differences and divide a population into different axes of variation. The software claims to “minimize spurious association while maximizing power to detect true association”.
In reading their website, the newer versions of the software also include a “fastmode option”, which can do everything more quickly. The software contains 3 directories, labelled “EIGENSTRAT”, “COVERTF”, and “POPGEN”. The script used by our lab is called “smartpca”, which is in the “POPGEN” directory.
Smartpca
The purpose of “smartpca” is to run PCA on input genotype data and output “eigenvectors” and “eigenvalues”. These are values that quantify the differences in individuals in the population.
Aside:
The readme file describes some nuances here which I don’t understand yet. Apparently, eigenvalue_k/(Sum of eigenvalues) is the proportion of variance explained by eigenvector_k. In addition, the method assumes that samples are unrelated, and if there are a small number of related individuals, they’ll be discarded as outliers.
Example:
- ../bin/smartpca -p parfile
The filetypes are the following:
- genotypename: input genotype file (in any format: see ../CONVERTF/README)
- snpname: input snp file (in any format: see ../CONVERTF/README)
- indivname: input indiv file (in any format: see ../CONVERTF/README)
- evecoutname: output file of eigenvectors. See numoutevec parameter below.
- evaloutname: output file of all eigenvalues
There are also many optional modifiers that can be used in the program. Of note, an optional modifier is “fastmode”, which is very important for making runtimes more realistic.
Estimaged running time:
- Without fast mode: 2.5e-12 * nSNP * NSAMPLES^2 hours if not removing outliers.
- E.g. for nSNPs = 600,000 and N = 20,000, running time is 600 hours = 25 days
- With fast mode: 1e-10 * nSNP * NSAMPLES hours
- E.g. for nSNPs = 600,000 and N = 20,000, running time is 1.2 hours
- Fastmode caveats: no outlier removal, no Tracy-Widom significance testing, no lsqproject mode, no F_st
The end result of EIGENSTRAT smartpca is eigenvectors and eigenvalues that quantify and divide subjects in the population. In graphical form, this is typically represented by “Principal component 1” (PC1) and “Principal component 2” (PC2). An example is provided below, in which a population was divided by PC1 and PC2:
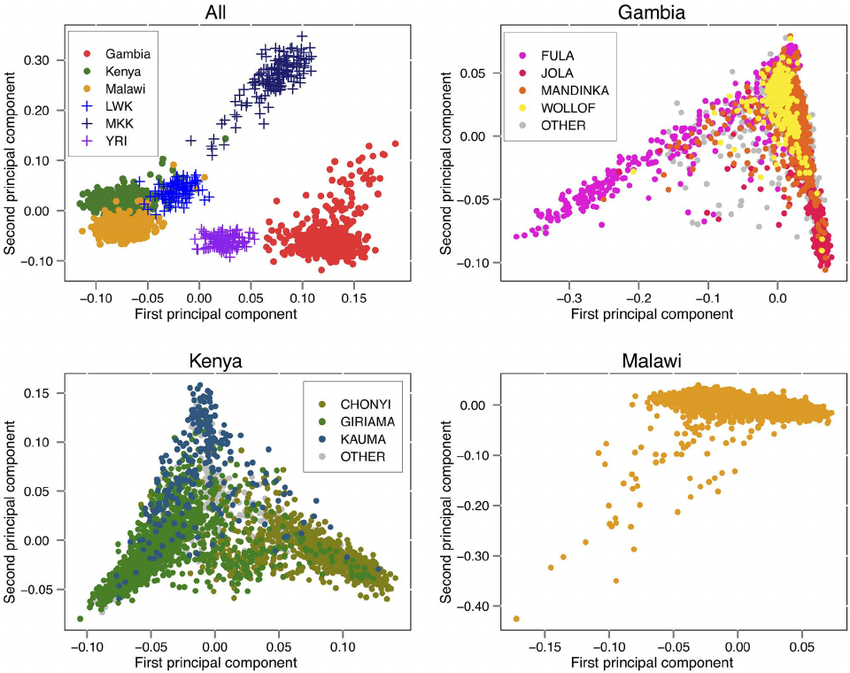
Links to EIGENSOFT information:
