Initial exploration of Penn Medicine Biobank
Published:
Today I’m exploring the data available within PMBB. This blog is a data dump of the directories and README files, which might not be pleasant to read. However, I’m interested in copying it here as a resource that I can check back on when navigating this complicated database.
To make things visual, I created a flowsheet illustrating the directories and files within PMBB.
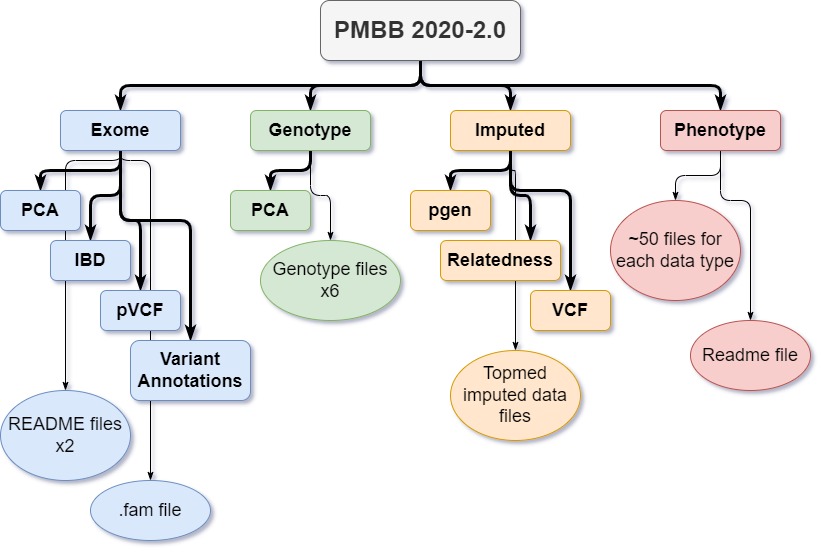
Directories
The PMBB is initially divided into different versions. The most recent version we’re working with is “PMBB-Release-2020-2.0”. For reference, it appears there are 4 versions so far, spanning 2017 to 2020.
My initial impression is that the different versions reflect updates for increasing patient numbers in the dataset and changing quality control measures for the genetic information.
Within “PMBB-Release-2020-2.0”, data is subdivided into 4 directories: Exome, Genotype, Imputed, and Phenotype. The remaining post will describe each of these directories and the README files within.
Exome directory
Contains 4 directories:
- PCA (Principle Components Analysis)
- Contains 4 exome files, differentiated by the names “ancestries”, “eigenval”, “eigenvac”, and “exome_SNPs_used_for_PCA”
- IBD (unsure of this acronym)
- Contains 7 files, named “2nd deg relationships”, “2nd deg unrelated”, “3rd deg relationships”, “3rd deg unrelated”, “full sibling relationships”, “num of relatives”, “parent child relationships”
- pVCF (.vcf are a form of SNP filetype)
- Contains 3 directories
- “All variants”, “GL_by_chrom”, “NF_by_chrom”
- 2 files “sample missingness” and “site_QC”
- Contains 3 directories
- Variant annotations
- 1 file named “Variant annotation counts”
Exome directory also contains 2 README files:
README-exome says:
Data Structure of Data Delivery (Freeze)
- /pVCF/ * Project level files, contains all 'QC pass' samples within the cohort. All variants are decomposed (one variant per line) and normalized. * NF data set is non-filtered. GL data set is filtered by 'GoldiLocks' filters as follows: > Filtering occurs in two major steps: I) Samples are filtered at particular variant sites > Sample genotype calls at sites carrying SNP variants are filtered using one criterion: 1) samples with depth of coverage at a particular SNP site (DP) < 7 have been changed to 'No-call' (./.). > Sample genotype calls at sites carrying INDEL variants are filtered using one criterion: 1) samples with depth of coverage at a particular INDEL site (DP) < 10 have been changed to 'No-call' (./.). II) Sites are filtered based on Allele Balance (AB) filters that are applied to all samples at a variant site. > Variant sites are omitted from the data set after sample specific filters have been applied and all appropriate samples have been changed to 'No-call' (./.). > Only sites where all samples carrying variation have Heterozygous (0/1) genotype calls, and all samples carrying the Het variation fail the Allele Balance (AB) cutoff are removed from the dataset. 1) SNP variant sites require at least one sample to carry an alternate Allele Balance (AB) >= 15%. 2) INDEL variant sites require at least one sample to carry an alternate Allele Balance (AB) >= 20% * /NF_by_chrom/ - NF pVCF files in standard VCF format with multiallelic representations spliced by chromosomes. Sample names are used as identifiers. * /GL_by_chrom/ - GL pVCF files in standard VCF format with multiallelic representations spliced by chromosomes. Sample names are used as identifiers. * /all_variants/ - NF plink files generated from NF pVCF, in standard bed/bim/fam format. Sample names are used in .fam file. - GL plink files generated from GL pVCF, in standard bed/bim/fam format. Sample names are used in .fam file. * _sample_missingness.tsv - Sample-level missingness file * _site_QC.txt.gz - siteQC file in gzip format for all GL sites - /Variant_annotation/ * PMBB-Release-2020-2.0_genetic_exome_variant-annotation-counts.txt - Columns 1-101 contain annotation of the GL variants using ANNOVAR including variant effect, in silico predictions, and allele frequencies in gnomAD. Information about the column names can be found in the ANNOVAR documentation (https://doc-openbio.readthedocs.io/projects/annovar/en/latest/) - Columns 102-104 contain homozygous/heterozygous counts produced by --geno-counts in PLINK. Column descriptions can be found at https://www.cog-genomics.org/plink/2.0/formats#gcount
README-IBD/PCA says:
Ancestry estimation
1. Took the intersection of SNPs between HapMap3 and the NF pVCF 2. Filtered to common, high quality SNPs (PLINK --maf 0.05 --geno 0.1 --snps-only; reported in *.commonSnps.SNPs_used_for_PCA.bim) 3. Merged NF pVCF for the HapMap3 dataset 4. Calculated the PCs for the HapMap3 samples and all non-HapMap3 samples onto those PCs 5. Trained a KDE for each ancestral superclass with the PCs of the HapMap3 samples. 6. Calculated the likelihood of each sample being from the different ancestral superclasses based on the KDEs. 7. For each sample, report the ancestral superclass based on the likelihoods. - If no superclass has a high enough likelihood, then report UNKNOWN0 - If one superclass has a high enough likelihood, then report that superclass - If 2 superclasses have a high enough likelihood (borderline samples), then report AFR over EUR, AMR over EUR, AMR over EAS, SAS over EUR, AMR over AFR; otherwise UNKNOWN1 (this is done to provide a stringent estimates of the EUR and EAS populations and inclusive estimates for the more admixed populations in our datasets) - If >2 superclasses have a high enough likelihood, then report UNKNOWN2 8. Reported each samples ancestry in *.commonSnps_samples_ancestries.txt IBD estimation 1. Filtered to high quality, common variants - Ran PLINK on the delivered NF pVCF bed/bim/fam files with --maf 0.1 --geno 0.05 --snps-only - We also filtered variants with abnormal het rates based on the expected vs observed het calculations (obs - exp > 0.01 or exp - obs > 0.1) 2. Filtered to high quality samples - Removed any sample with percent 20x coverage < 0.75 or Dstat (see below for a description) > .12 (see attached list of low quality samples excluded from the relationship) 3. Calculated IBD estimates among individuals within the same ancestral superclass (e.g. AMR, AFR, EAS, EUR, SAS). This allows for more accurate relationship estimates, but misses relationships between individuals with different ancestral backgrounds. - Calculated with PLINK using the minimum PI_HAT cutoff of 0.1875 to capture out to 2nd degree relationships 4. Calculated IBD estimates among all individuals using a minimum pi-hat cutoff of 0.3 to get the more easily estimate 1st degree relationships among all samples (--min 0.3) 5. Grouped the individuals into 1st degree family networks using the first degree relationships from step 4 6. Ran each first degree family network from step 5 through the prePRIMUS pipeline built into PRIMUS using default setting - prePRIMUS identified all HapMap3 populations that most closely matches the ancestries of the samples in each 1st degree family network and uses those populations to infer allele frequencies - This process gets improved IBD estimates for the relationships within each family network and catches close relationships that span more than one ancestral superclass - This process typically captures 1st degree relationships, but may capture out to 3rd degree relationships if they exist within a 1st degree family network 7. Combined IBD estimates from step 3 and step 6 to make *.NF.pVCF.genome by taking the IBD estimates from step 3 and then adding any IBD estimates from step 6 that were not already in the IBD estimates from step 3 Stat QC metricThe Dstat is a QC metric used to identify samples with evidence of contamination that may cause problems with downstream analyses. The Dstat metric is calculated by comparing the allele balance distribution for each sample to a reference distribution; it uses the K-S (Kolmogorov-Smirnov) test’s D-statistic as the QC metric. We have empirically determined that a cutoff value of 0.12 removes the problematic samples while retaining the greatest number of high quality samples. The het-hom and D-stat generally agree with each other.
Lastly, the exome directory contains 1 file called “PMBB-Release-2020-V2.0_genetic_exome.fam”. I presume the .fam stands for family.
Genotype directory
This directory has 6 files with different file extensions. I presume they’re the same file, but in different genotype formats. The filetypes are: .bed, .bim, .fam, .hh, .log, .vcf.gz, and .vcf.gz.tbi
It also has one subdirectory named “PCA”
The subdirectory “PCA” contains 2 files named “ancestries.txt” and “genotype.eigenvec”.
Imputed directory
Contains no files. Contains 3 subdirectories named:
- pgen
- Contains files for each chromosome named “topmed-r2”
- For each file, there are 3 file extensions “.pgen”, “.psam”, and “.pvar”
- Relatedness
- Contains 2 files named “topmed-r2-IBD.genome” and “topmed-r2-relateds-droplist.txt”
- vcf
- Contains files for each chromosome named “topmed-r2”
Phenotype directory
I saved the best for last! This one is easy to understand as it contains electronic health record data for all patients.
It contains many files, divided into data for:
- Covariates
- Demographics
- ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes
- HbA1c
- Albumin
- ALP
- ALT
- AST
- Bands-Con
- Bands-PCT
- Basophils-Con
- Basophils-PCT
- CK
- CRP
- Direct bilirubin
- Eosinophil-Con
- Eosinophil-PCT
- ESR
- Fasting glucose
- GGT
- HDL
- Indirect bilirubin
- INR
- LDL
- Lymphocyte-Con
- Lyphocyte-PCT
- Median-matrix
- Metamyelocyte
- Monocyte-Con
- Monocyte-PCT
- Myelocyte
- Platelets
- Promyelocyte
- PTT
- Random glucose
- SC
- Total bilirubin
- Total cholesterol
- Triglycerides
- Urobilinogen
- WBC count
- Medications part 1, 2, and 3
- Phecode
- Procedure codes
- Smoking history
- BMI
- Blood pressure
- Weight
Of course, each file contains non-identifiable patient IDs that allow their data to be linked across files and genotypic data
There is also a README file, copied below:
Date Range: 01/01/2005-07/01/2020
Data Types: - Demographics - Diagnosis
- Procedures
- Select Labs
- Select Medications
- Vital Signs
- Social History
Demographics:
- PMBB-Release-2020-2.0_phenotype_demographics.txt – Demographics data (Gender, Race, Hispanic_Ethnicity, Shifted birth date) - PMBB-Release-2020-2.0_phenotype_covariates.txt – Covariate information including genetically inferred Sex (from RGC), Birth Year, Age at PMBB Enrollment Date, Genetically Inferred Ancestry (from RGC), and first 10 PCs (from RGC). ** Notes: Diagnosis:
- PMBB-Release-2020-2.0_phenotype_icd.txt – ICD-9 and ICD-10 diagnoses codes (excluding sensitive codes) - PMBB-Release-2020-2.0_phenotype_icd-*-matrix.txt – Code counts in matrix form for ICD-9 and ICD-10 format 5-digit codes. Mapping described below. - PMBB-Release-2020-2.0_phenotype_phecode.txt – ICD-9 and ICD-10 diagnosis codes annotated with phecode information ** Notes: - Two summary matrices with the code count for each patient have been provided, one for ICD-10 and one for ICD-9 codes. In both cases, codes were mapped to the respective vocabularies using CMS General Equivalence Mappings; codes with no mapping for that vocabulary were dropped. - Phecodes were mapped using https://github.com/PheWAS/PheWAS/ R package. Exclusions were not applied. Procedures:
- PMBB-Release-2020-2.0_phenotype_procedure-codes.txt – CPT, ICD-9 and ICD-10 procedure codes
Vital Signs:
- PMBB-Release-2020-2.0_phenotype_vitals-BMI.txt – Body Mass Index
- PMBB-Release-2020-2.0_phenotype_vitals-DBP.txt – Diastolic Blood Pressure
- PMBB-Release-2020-2.0_phenotype_vitals-Weight.txt – Weight
Labs:
- PMBB-Release-2020-2.0_phenotype_labs-A1C.txt – Hemoglobin A1C
- PMBB-Release-2020-2.0_phenotype_labs-ALB.txt – Albumin levels
- PMBB-Release-2020-2.0_phenotype_labs-Alkphos.txt – Alkaline Phosphatase
That’s it! I hope to make future blog postings on additional papers that cover analaysis of genetic information and manipulating genetic data with R.
